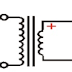
An A.C. electrical device used to change high voltage low
current A.C. into low voltage high current A.C. and vice-versa without
changing the frequency.
In brief,
1. Transfers electric power from one circuit to another.
2. It does so without a change of frequency.
3. It accomplishes this by electromagnetic induction.
4. Where the two electric circuits are in the mutual inductive influence of
each other.
Principle of operation:
It is based on the principle of Mutual induction. According to which an
e.m.f. is induced in a coil when the current in the neighboring coil changes.
The winding to which a.c output voltage is impressed is called the primary
of the transformer and the winding across which the load is connected is
called the secondary of the transformer.
Construction of Transformer:
1.Basically, it consists of two inductive windings(Primary and secondary winding) and a laminated steel core. The coils are insulated from each other as well as from the steel core.
2.the core is constructed by attaching or assembling laminated sheets of steel with a minimum air gap to achieve an unrestricted continuous magnetic path.
3.the primary and secondary coils are wound on ferromagnetic metalcore.
4.The function of the core is to transfer changing magnetic flux from the primary coil to the secondary coil.
5.The primary winding has N1 numbers of turns and secondary winding has N2 numbers of turns, the numbers of turns play a major important role in the function of the transformer.
6.silicon steel is used to provide high permeability and low hysteresis loss.
7.Laminated sheets are to reduce eddy current loss.
Working:
1.When current in primary winding coil changes being alternating in nature a changing magnetic field produced.
2.The changing magnetic field gets associated with the secondary coil through the soft iron core.
3.hence magnetic flux linked with secondary coil changes.
4.which induced emf in the secondary coil.
Type of Transformers:
They are classified on the basis of construction, types of cooling, etc.
(a). On the basis of construction, it can be classified into two types.
(i). Core type transformer
(ii). Shell type transformer
(i). Core type transformer:
1.Cylindrical form winding is wrapped around two sides of the laminated square core.
2.The cylindrical coils have different layers and each layer are insulated from each other.
for insulation material are used as paper, cloth, or mica.
3.Low voltage windings are placed near to the core and easier to insulate.
(ii). Shell type transformer:
windings are wrapped around the center leg of the laminated core.
it may have a simple rectangular form or
it may have a distributed form.
windings are wrapped around the center leg of the laminated core.
it may have a simple rectangular form or
it may have a distributed form.




No comments:
Post a Comment